Neurovascular Imaging
- Home
- Neurovascular Imaging
What is Neurovascular Imaging
Symptoms
- Headaches
- Sudden or gradual changes in vision, including blurriness, double vision, or loss of vision
- Weakness or numbness
- Speech difficulties
- Balance and coordination problems
- Memory problems or confusion
We offers a comprehensive suite of advanced imaging modalities to provide precise and detailed assessments of neurovascular anatomy
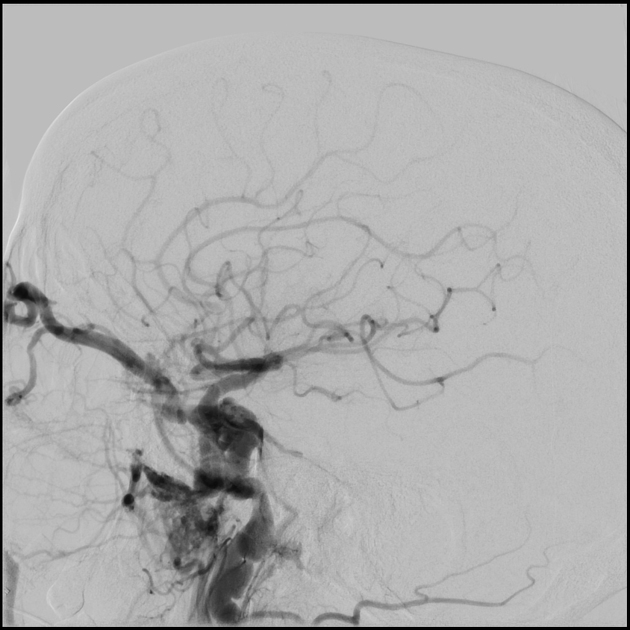
Catheter Angiography
High-Resolution Imaging: DSA provides high-resolution images of blood vessels, allowing for precise visualization of vascular lesions such as aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), and stenoses.
Dynamic Assessment: DSA enables dynamic assessment of blood flow dynamics, including the detection of vascular abnormalities such as fistulas and hemodynamic changes associated with ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.
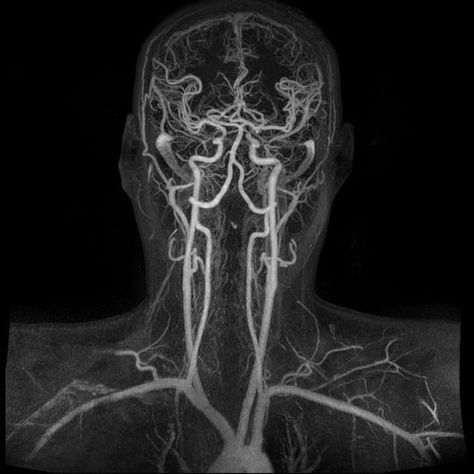
Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
Non-Invasive Assessment: MRA allows for non-invasive assessment of vascular anatomy, providing detailed images of arteries and veins without the need for contrast agents or radiation exposure.
Multiplanar Imaging: MRA offers multiplanar imaging capabilities, enabling visualization of blood vessels from various angles and perspectives, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning.

Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA)
High-Resolution Imaging: CTA provides high-resolution images of vascular structures, allowing for the detection and characterization of vascular lesions such as aneurysms, dissections, and thrombi.
Rapid Acquisition: CTA offers rapid acquisition times, making it well-suited for emergent evaluation of acute cerebrovascular conditions such as ischemic stroke or intracranial hemorrhage.

Perfusion Imaging
Assess Tissue Viability: Perfusion imaging assesses tissue perfusion and oxygenation, helping to identify areas of hypoperfusion or ischemia in acute stroke patients and guide treatment decisions.
Evaluate Treatment Response: Perfusion imaging can also be used to evaluate treatment response following interventions such as thrombolysis or endovascular thrombectomy, providing insights into tissue reperfusion and functional recovery.
Carotid Doppler Ultrasound
Detect Stenosis: Carotid Doppler ultrasound detects and quantifies the degree of stenosis in the carotid arteries, providing valuable information for risk stratification and treatment planning in patients with carotid artery disease.
Carotid Doppler ultrasound can also be used to monitor disease progression over time, allowing for early detection of changes in carotid artery patency and the initiation of appropriate interventions

Frequently Asked Questions
Neurovascular imaging encompasses various imaging techniques used to visualize blood vessels and related structures in the brain and spinal cord. It is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring conditions such as aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), and strokes, enabling timely intervention and treatment planning.
Catheter angiography, also known as digital subtraction angiography (DSA), is an invasive procedure that provides high-resolution images of blood vessels using contrast dye and X-rays. MRI and CT scans are non-invasive imaging techniques that use different principles to generate detailed images of the brain and blood vessels.
Neurovascular imaging may be recommended for patients presenting with symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, visual disturbances, or neurological deficits suggestive of vascular pathology. It is also used for monitoring patients with known vascular conditions or as part of pre-operative planning for neurosurgical procedures.
Perfusion imaging provides insights into cerebral blood flow and tissue perfusion, aiding in the identification of areas of ischemia or hypoperfusion in stroke patients. This information helps guide treatment decisions, such as determining eligibility for thrombolytic therapy or endovascular thrombectomy.
Carotid Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique used to assess blood flow in the carotid arteries, which supply blood to the brain. It can detect narrowing (stenosis) or blockages in these arteries, helping identify individuals at risk of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
While neurovascular imaging procedures are generally safe, there are potential risks such as allergic reactions to contrast dye, exposure to radiation in CT scans, or complications related to catheter angiography, such as bleeding or blood vessel injury. However, the benefits of obtaining crucial diagnostic information often outweigh these risks, especially when performed by experienced specialists like Dr. Santosh B. Patil.

