Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
- Home
- Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
What is Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
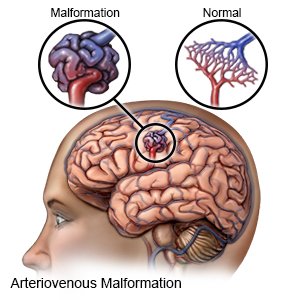
Symptoms of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
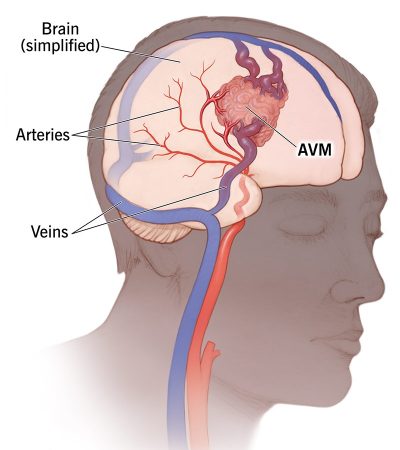
- Seizures
- Headache.
- Muscle weakness or complete paralysis
- Nausea and vomiting
- Numbness or tingling sensation
- Problems with movement, speech, memory, thinking, balance or vision
We offers a comprehensive and Multidisciplinary approach to managing these Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
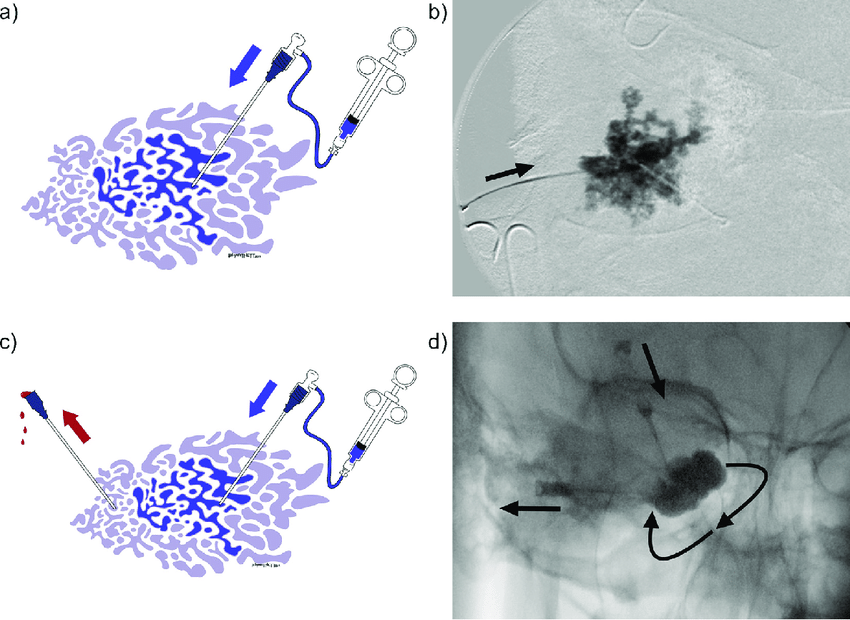
Endovascular Embolization using Glue/Onyx
Glue Embolization
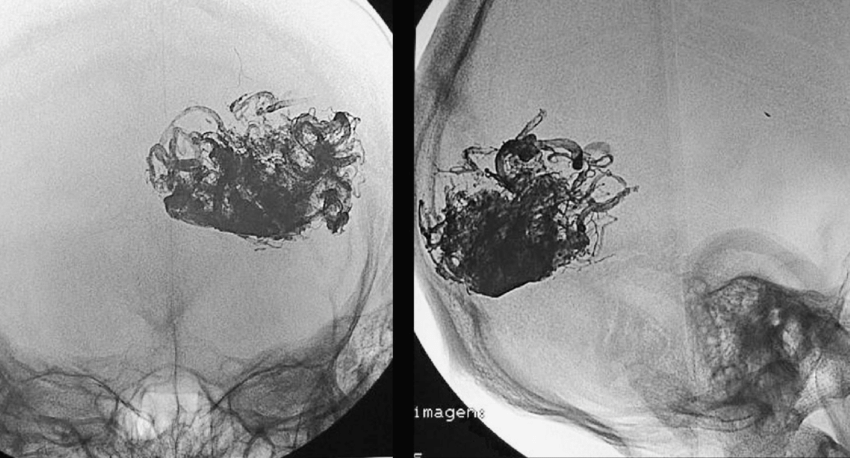
Onyx Embolization
Surgical Excision
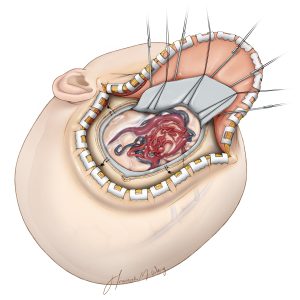
Stereotactic Radiosurgery
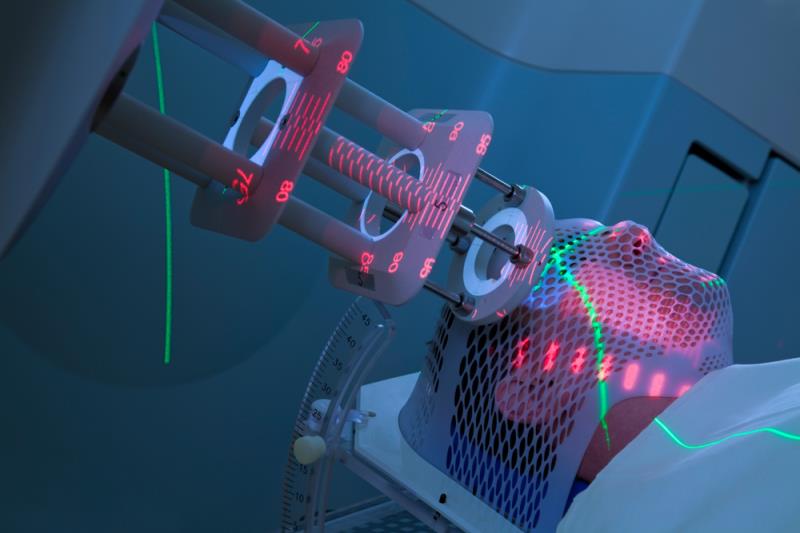
Dr. Patil collaborates closely with neurosurgical colleagues to perform surgical excision & Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS).
Head & Neck Vascular Malformation
Frequently Asked Questions
A cerebral AVM is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels in the brain that disrupts normal blood flow and increases the risk of bleeding or stroke. A dural AVF is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins in the dura mater, the outer covering of the brain.
Symptoms can vary widely depending on the location and size of the lesion but may include seizures, headaches, neurological deficits (such as weakness or numbness), visual disturbances, or symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Diagnosis typically involves imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), or digital subtraction angiography (DSA). These tests help visualize the abnormal blood vessels and assess the extent of the lesion.
Treatment options may include endovascular embolization using glue or onyx, surgical excision, radiosurgery, or a combination of these approaches. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the size, location, and complexity of the lesion, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Risks may include bleeding, stroke, infection, or damage to surrounding brain tissue. However, the benefits of treatment, such as reducing the risk of hemorrhage or alleviating symptoms, often outweigh the potential risks, especially in symptomatic patients.
The prognosis depends on various factors, including the size and location of the lesion, the effectiveness of treatment, and the presence of any complications. With appropriate treatment and follow-up care, many patients can experience symptom relief and lead fulfilling lives with reduced risk of complications.
We offers a comprehensive and Multidisciplinary approach to managing these Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation

