Cerebral Aneurysm
- Home
- Cerebral Aneurysm
What is Cerebral Aneurysm
Under the expert care of Dr. Santosh B. Patil, patients benefit from a comprehensive range of advanced interventions tailored to manage cerebral aneurysms effectively.
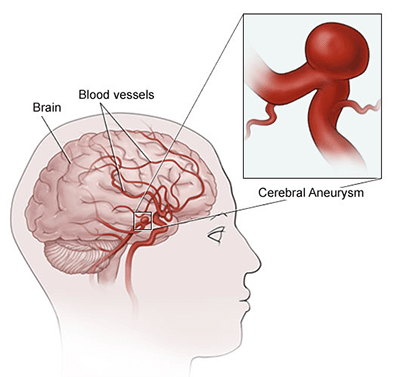
Symptoms of Cerebral Aneurysm
- Headaches & Eye Pain
- Vision changes
- Diminished eye movement
- Stiff neck
- Nausea and vomiting
- Changes in mental status, such as drowsiness
- High blood pressure
We provide comprehensive range of advanced interventions to manage cerebral aneurysms effectively which reduces the risk of rupture and rebleeding.
Cerebral Aneurysm
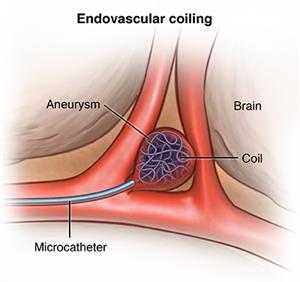
Endovascular Coiling
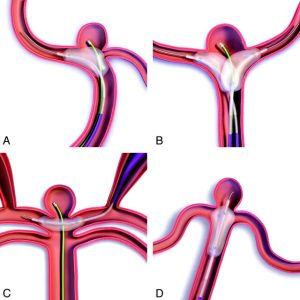
Balloon Remodeling
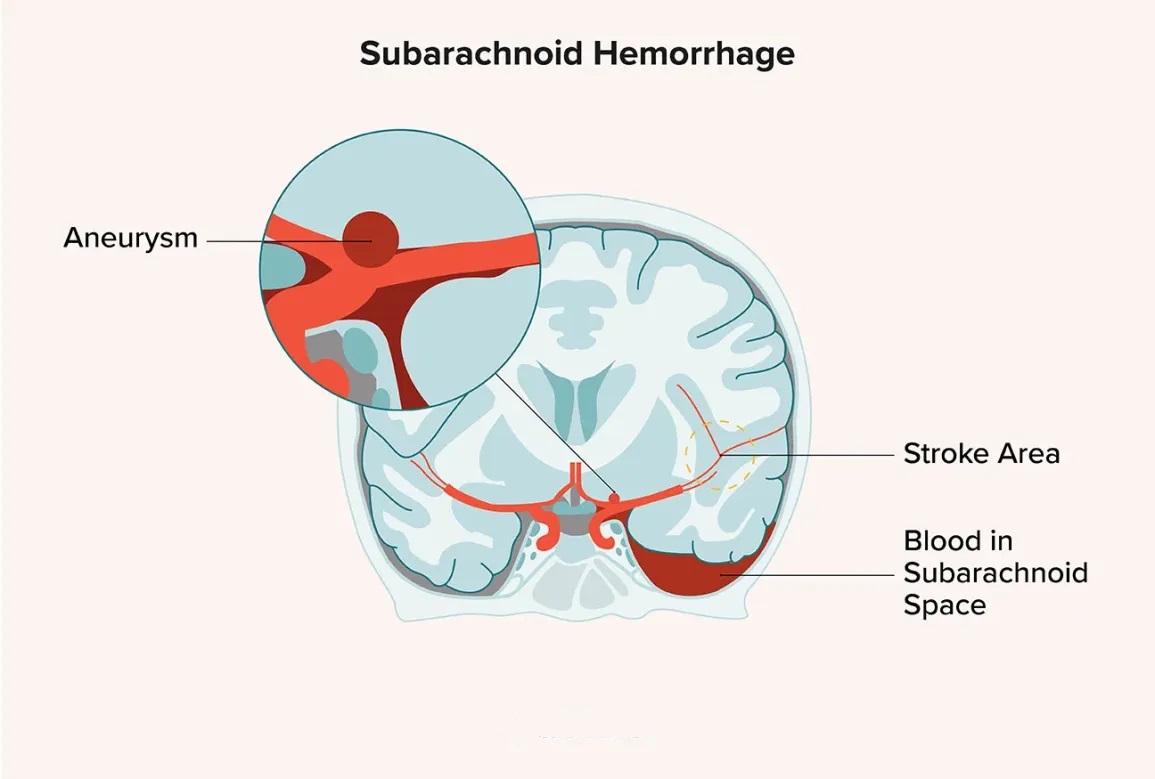
Integrated Neurovascular Unit for Acute Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
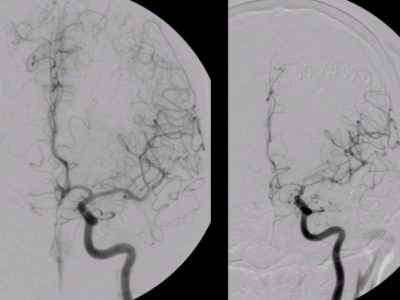
Cerebral Vasospasm Management
Intra-Arterial Chemical Vasodilatation
Flow Diverter Stenting
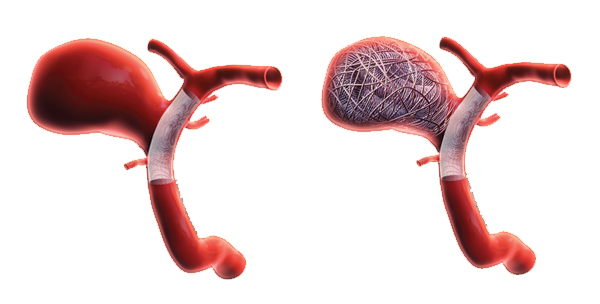
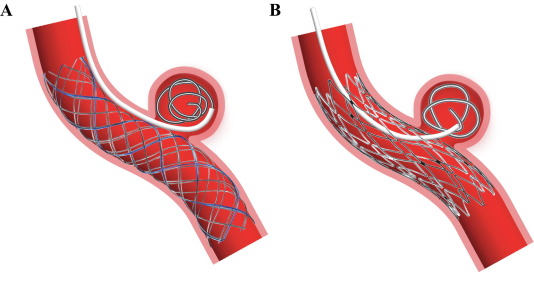
Stent-Assisted Coiling
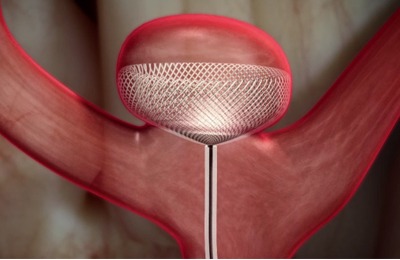
Web Device
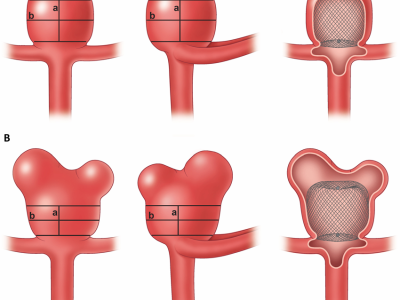
Contour Device
By offering a comprehensive suite of interventions for both cerebral aneurysm management and cerebral vasospasm, Dr. Santosh B. Patil demonstrates his commitment to providing patients with the highest standard of care, leveraging innovative techniques to optimize outcomes and enhance quality of life for individuals affected by these challenging neurovascular conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Symptoms may include severe headaches, vision changes, numbness or weakness on one side of the face or body, and difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
Treatment depends on factors such as the size and location of the aneurysm, the patient’s overall health, and the risk of rupture. Options may include observation, endovascular coiling, clipping, or flow diversion.
Endovascular coiling involves inserting a catheter into the blood vessels and placing detachable coils within the aneurysm to promote clotting and reduce the risk of rupture. Surgical clipping involves placing a metal clip at the base of the aneurysm to prevent blood flow into it.
Risks may include bleeding, infection, stroke, or complications related to anesthesia. However, the benefits of treatment often outweigh the risks, especially in cases where the aneurysm poses a high risk of rupture.
The long-term prognosis depends on factors such as the size and location of the aneurysm, the effectiveness of treatment, and the presence of any complications. With appropriate treatment and follow-up care, many patients can lead fulfilling lives with reduced risk of aneurysm rupture.
Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, avoiding smoking, and controlling high blood pressure can help reduce the risk of developing or rupturing cerebral aneurysms. Additionally, seeking prompt treatment for conditions such as polycystic kidney disease or connective tissue disorders may also be beneficial.

