Arteriovenous Fistula
- Home
- Arteriovenous Fistula
What is Arteriovenous Fistula
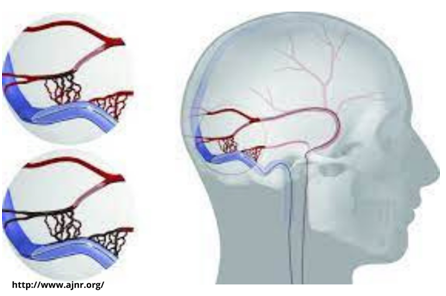
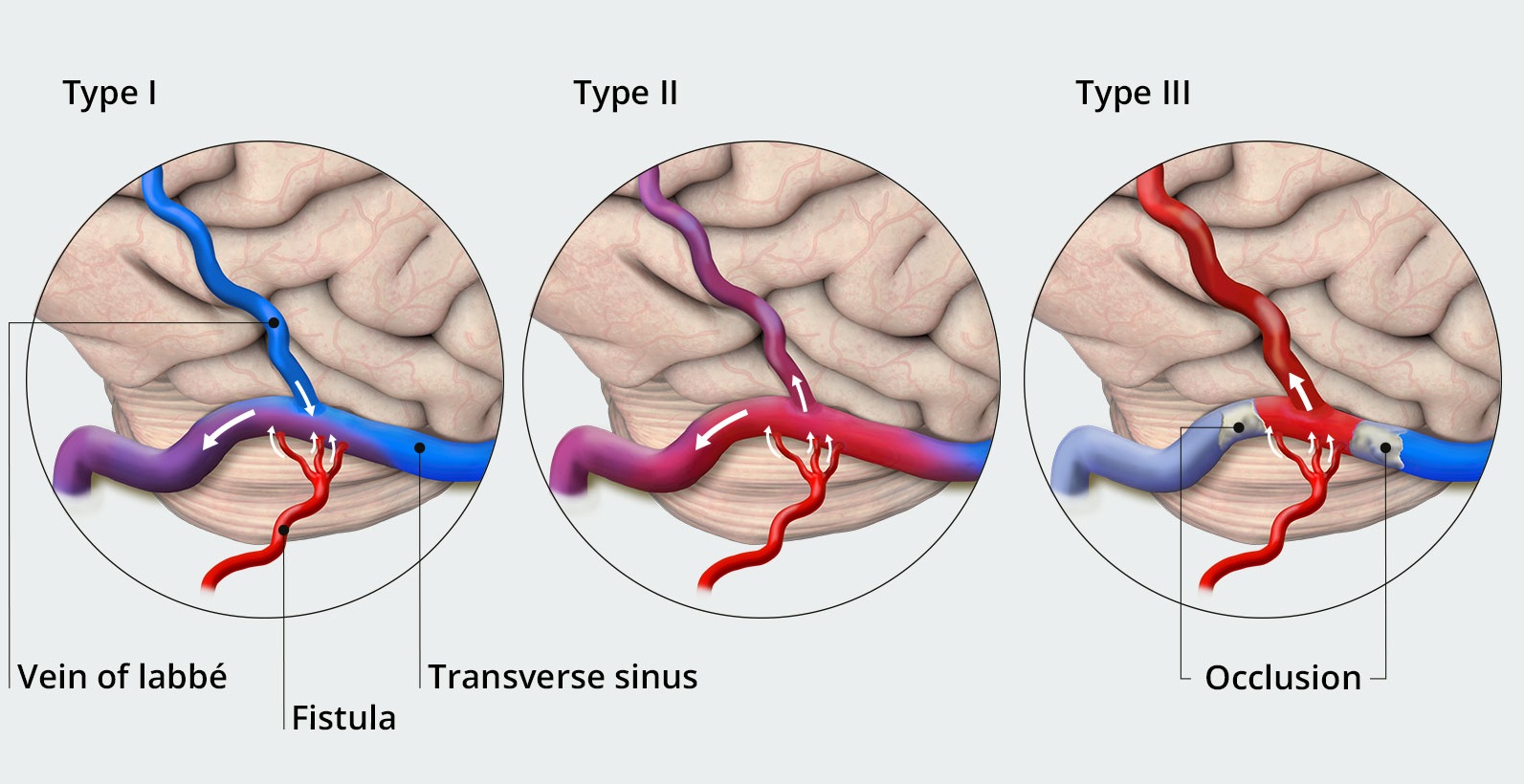
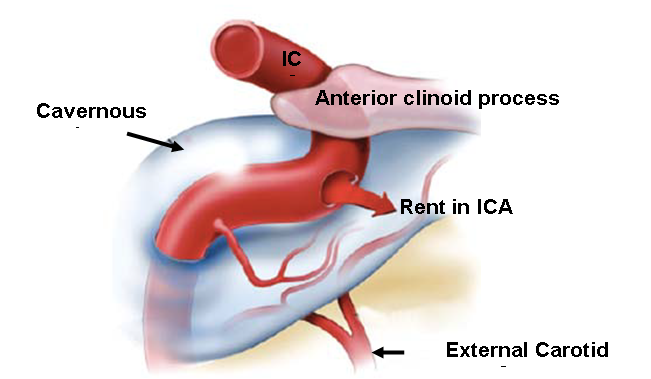
There are two major types of AVFs: dural AVFs and carotid-cavernous fistulas (CCFs). These are acquired lesions, which means that patients are not born with them, but instead develop them later in life. They can be a result of infection or traumatic injuries, but most develop without any specific cause.
Symptoms of Arteriovenous Fistula
- Purplish, bulging veins seen through the skin, similar to varicose veins
- Swelling in the arms or legs
- Decreased blood pressure
- Fatigue
- Heart failure
We provide minimally invasive techniques in order to reduce risk of Arteriovenous Fistula
Arteriovenous Fistula
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula (DAVF)
Caroticocavernous Fistula
Frequently Asked Questions
Arteriovenous Fistula can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired due to trauma, surgery, or underlying conditions such as vascular malformations. Congenital AVFs may develop during fetal development, while acquired AVFs can result from injuries or medical procedures that disrupt normal blood vessel anatomy.
Symptoms of Arteriovenous Fistula can vary depending on the location and size of the abnormal connection. Common symptoms may include swelling, pain, warmth, pulsatile mass, or changes in skin color or temperature. In cases of cerebral AVFs, symptoms may include headaches, seizures, neurological deficits, or intracranial hemorrhage.
Diagnosing Arteriovenous Fistula typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies. Imaging modalities such as angiography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), computed tomography angiography (CTA), or ultrasound may be used to visualize the abnormal blood flow and assess the location, size, and associated complications of the AVF.
Treatment options for Arteriovenous Fistula depend on various factors, including the location, size, symptoms, and overall health of the patient. Treatment may include minimally invasive procedures such as endovascular embolization, surgical excision, radiosurgery, or observation and monitoring. The choice of treatment is tailored to each patient’s specific needs and the characteristics of the AVF.
While Arteriovenous Fistulae can cause significant symptoms and complications, they are not always life-threatening. However, depending on the location and severity of the AVF, it can lead to serious complications such as hemorrhage, organ damage, or neurological deficits if left untreated. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are essential to prevent potential complications and improve outcomes.
The risk of recurrence of Arteriovenous Fistula after treatment depends on various factors, including the type of treatment, the size and location of the AVF, and individual patient factors. In some cases, particularly with large or complex AVFs, recurrence may occur despite successful initial treatment. Close monitoring and follow-up evaluations are important to detect any recurrence early and intervene as needed.

